SDG2030: Challenges of technological applications in advancing Global Goals
Application of contemporary and future information technologies may go milestones in advancing sustainable development goals (SDGs) provided the challenges are overcome and implementation is ensured.
- Country:
- United Kingdom
HIGHLIGHT
- 3 billion people worldwide lack clean cooking fuels and technology.
- Out of total global energy consumption, only 17.5 percent comes from renewable energy.
- Ocean activity has increased by 26 percent since pre-industrial levels and is expected to increase by a further 125 percent by 2100.
- Land degradation is affecting 20 percent of earth’s land area and lives of 1 billion while the risk of species extension has worsened by almost 10 percent in the past 25 years.
As experts from throughout the world have started to admit the non-feasibility of complete achievement of all the targets of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set up by the United Nations for the year 2030, there is an increasing emphasis on achieving the maximum possible targets through contemporary and future technological interventions. However, the application of these technologies has certain pre-requirements and challenges.
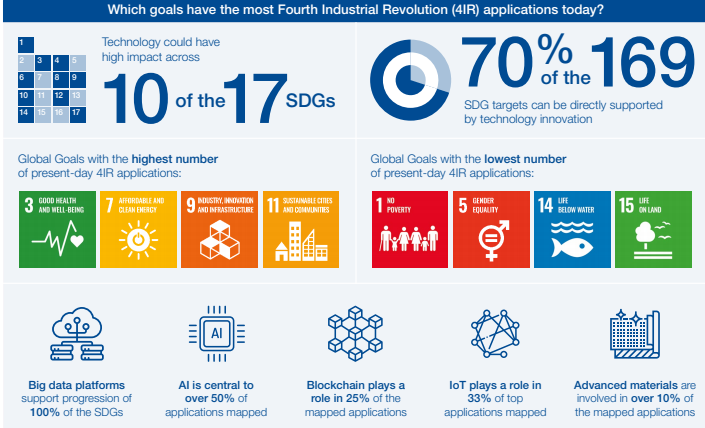
According to a recent study conducted by the PWC (PricewaterhouseCoopers) titled ‘Unlocking Technology for Global Goals’ it was revealed that the use of technology is minimum in four SDGs. They are SDG 1 for No Poverty, SDG 5 for Gender Equality, SDG 14 for Live Below Water and SDG 15 for Life on Land. The report has emphasized that technology could have high impacts across 10 out of 17 SDGs and 70 percent of the 168 targets. The global goals having a maximum scope of technological applications such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (MI), Blockchain and 5 G internet, etc. are No Poverty (SDG1), Good Health and Well Being (SDG3), Quality Education (SDG4), Water and Sanitation (SDG6), Decent Work and Economic Growth (SDG8), Reduced Inequalities (SDG10), Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG12), Life Below Water (SDG14) and Partnerships for the Goals (SDG17). After mapping over 300 applications to advancing the global goals, the study has presented four barriers. They are – data, technology, people and process.
Data: Data collection is a predominating issue in almost all the countries that are lagging in achieving SDGs. No information technology could ever produce desired results if it is fed with wrong or incredible data. Production of credible data requires credibility from data collection, analysis and its final presentation in a usable format.
Technology: The study revealed that about 80 percent of technological equipment and tools throughout the globe require internet connectivity while 90 percent of technology requires electricity. Therefore, internet connection and electricity are prerequisites for technological applications in advancing SDGs. Besides, the maturity of technological solutions also varies from country to country and across the regions within the country.
People: The use of technology depends on technical education and training of the population. There exists a huge talent gap in the technical training of people in developing and developed countries. The obstacles in education such as lack of access to education, insufficient funding, lack of infrastructure, lack of experts for training, etc are the main hurdles in providing technical skills to people for proper use of technology. Besides, skill training is also required to accommodate the human resource to be replaced after technological interventions. It is estimated that it will take an investment of $19.9 billion for the US government to reskill 77 percent of workers expected to be displaced by technology.
Process: Technological applications will also require a change in governance and regulatory mechanism. Before opting for a technological transformation, the government will need to put up a system in place for proper regulation to ensure privacy and data security.
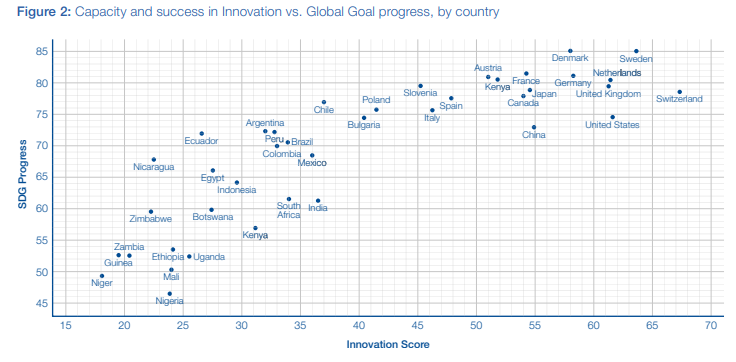
The report has also graded 41 countries on the basis of innovation score and SDG progress. In the list, Switzerland has scored a maximum 65 points on innovation scores for technological applications while Sweden and Denmark are on top of SDG progress. Nigeria has been ranked at the lowest level in terms of SDG progress while Niger has scored a minimum in innovation.
Technological application is a multi-dimensional process. Besides the initial requirements, it needs identification of operational, societal, technological advancement and other risks as well. These risks emerge in the course of time for which enhanced technological education is required to replace the existing technologies with the new ones. The report presents a detailed route map for technological applications in advancing the SDG 2030. Besides, it has also divided the technologies into three categories – high maturity, medium maturity, and low maturity – as per the requirement of the concerned countries.
The report also highlights that the world is not on track to end poverty by 2030 as at least 6 percent of the people will be under extreme poverty. Besides, two-third of under-nourished people worldwide live in sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia. The report has identified 13 core fourth industrial revolution technologies that could be used in advancing SDGs. They are – Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, Internet of things, Big Data, Advanced Materials, Robotics, Augmented/ Virtual Reality, 3 D Printing, Drones, 5 G, and Synthetic Biology.
(Disclaimer: The opinions expressed are the personal views of the author. The facts and opinions appearing in the article do not reflect the views of Devdiscourse and Devdiscourse does not claim any responsibility for the same.)
- FIRST PUBLISHED IN:
- Devdiscourse










