Reducing inequalities in access to WASH: How innovation is leading the way?
Despite making significant strides, a significant portion of the world population, especially the poor, still lack access to reliable and safe drinking water, toilets, and other basic facilities.
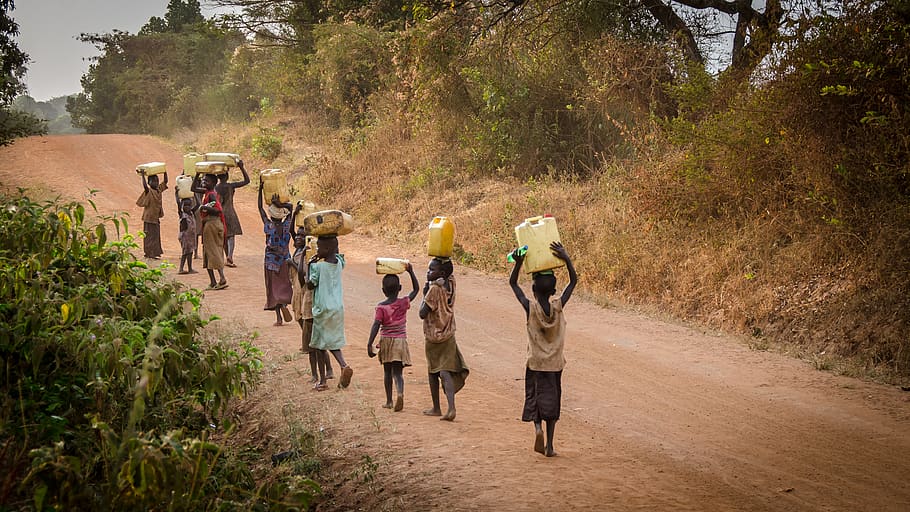

Access to Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) has been recognized as a fundamental human right. It is inevitably interlinked with many of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and is crucial to the individual and socio-economic development.
According to the United Nation statistics, by 2025, 1.8 billion people will be living in countries or regions with absolute water scarcity, and two-thirds of the world's population could be living under water-stressed conditions. Unfortunately, the quality and quantity of water is decreasing day by day owing to various factors including rapid urbanization, industrial waste, population growth, unsafe disposal of human waste and climate change.
Inadequate hygiene, water quality, and poor sanitation practices directly affect individual, public health and the environment as well. Despite making significant strides, a significant portion of the world population, especially the poor, still lack access to reliable and safe drinking water, toilets, and other basic facilities.
Digital technology-based solutions can help promote access to clean WASH services for all people throughout the world, regardless of their geographic locations. Here are a few real-world examples of how innovation is changing the way basic services are delivered.
Pit Vidura
Unsafe water and poor sanitation practices may result in dangerous diseases such as cholera, dysentery, viral hepatitis, skin and eye infections such as trachoma, resulting in up to 432 000 diarrhoeal deaths annually. According to a 2019 UN report on the plight of sanitation workers, millions of sanitation workers in the developing world are forced to work in conditions that endanger their health and lives and violate their dignity and human rights.
Pit Vidura, a Rwanda-based sanitation logistics company develops the hardware, software, and payment systems to streamline the waste collection in low-income dense urban settlements of Kigali, Rwanda and make safe and affordable services available for all.
The company has developed innovative systems and services to make the collection and emptying of fecal waste safe, clean, efficient, and affordable, in hard-to-reach areas. As opposed to the traditional practice of manually emptying pit latrines, Pit Vidura utilizes a double vacuum pumping system, DoVac, to pull waste from a distance of up to 200 meters.
The company hires former manual scavengers and equip them with professional emptying tools and training to provide safe and hygienic services. It has also developed IT tools to facilitate clustered service delivery which minimizes transport costs and makes our service more efficient and affordable for low-income households.
MajiData
MajiData, a joint initiative of the Kenyan Water Services Regulatory Board (WASREB) and the Water Sector Trust Fund (WSTF) aims to contribute to a progressive improvement of water and sanitation services in Kenya’s urban low-income areas.
Designed to serve the data needs of several target groups, the MajiData portal provides up-to-date maps of all regulated water utilities and all low-income areas within the service areas of the utilities in Kenya. It also provides georeferenced information on all infrastructure and key performance indicators.
PiQuant
Inadequate, or inappropriately managed water resources and sanitation services pose several health risks. Ingestion of contaminated water can expose people to a wide range of diseases such as diarrhea, arsenicosis or fluorosis.
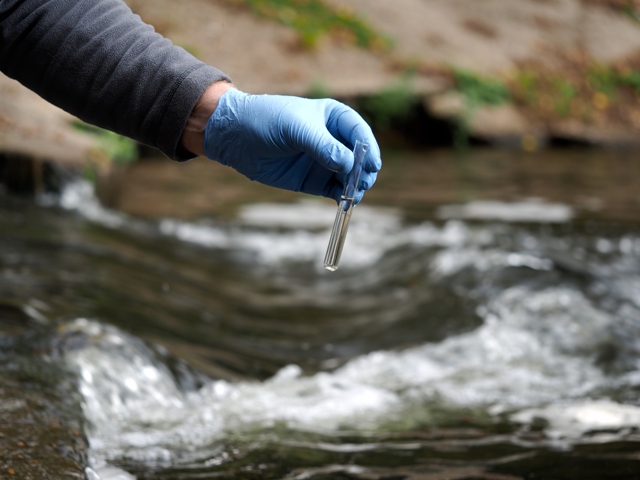

PiQuant, a healthcare IoT solution company has developed a Water Scanner to detect bacteria, heavy metals, and chemicals in a water sample in less than 10 minutes, anytime, anywhere. The device is accompanied by a Monitoring System that collects or shares data and categorizes it in central datacenters to produce a real-time regional water quality map for rapid response.
Other application areas of PiQuant’s Water Scanner include testing water pipe conditions in urban settlements and analyzing the cause of water pollution, testing urine to monitor everyday health conditions, checking water safety in purifiers and checking the contamination level while producing beverages.
Fresh Life Initiative
In Nairobi, over 2 million people reside in urban slums with limited access to water and sanitation services. To solve the crisis, Nairobi-based Sanergy develops bold sanitation and waste management solutions to address all systemic gaps from waste containment, emptying, transport, treatment, and reuse.
Sanergy has installed over 3,000 container-based sanitation units called Fresh Life Toilets across Nairobi’s urban slums, serving 133,680 residents per day with safe sanitation. Each high-quality, low-cost unit comprises a urine-diverting squat plate, handwashing station with soap, water and a bin for feminine hygiene products. They also provide operational support and a daily waste collection service.
 Image Credit: Twitter (@DFCgov)
Image Credit: Twitter (@DFCgov)
Sanergy is now developing innovative solutions including a digital customer service platform to collect critical data that will help them manage, and operate even more efficiently, whilst enhancing customer satisfaction. The Fresh Life Initiative seeks to have an active network of 4,900 Fresh Life Toilets that will serve approximately 36 percent of the population in Mukuru slum.
Akvo Caddisfly
Akvo Caddisfly is a simple, fast, portable and smartphone-based low-cost drinking water testing kit to quickly analyze the level of fluoride, free Chlorine, salinity, and various other parameters in drinking water. Using smartphone water testing can be affordable with data immediately accessible and shareable online, as opposed to lab-based tests that are expensive and often cause delays.
Akvo has developed its own electrical conductivity (EC) sensor which can be simply dipped in water to know the level of total dissolved solids (TDS) in the water, an indication of salinity. The platform can also be used to calculate the most probable number of E.coli per 100 ml.
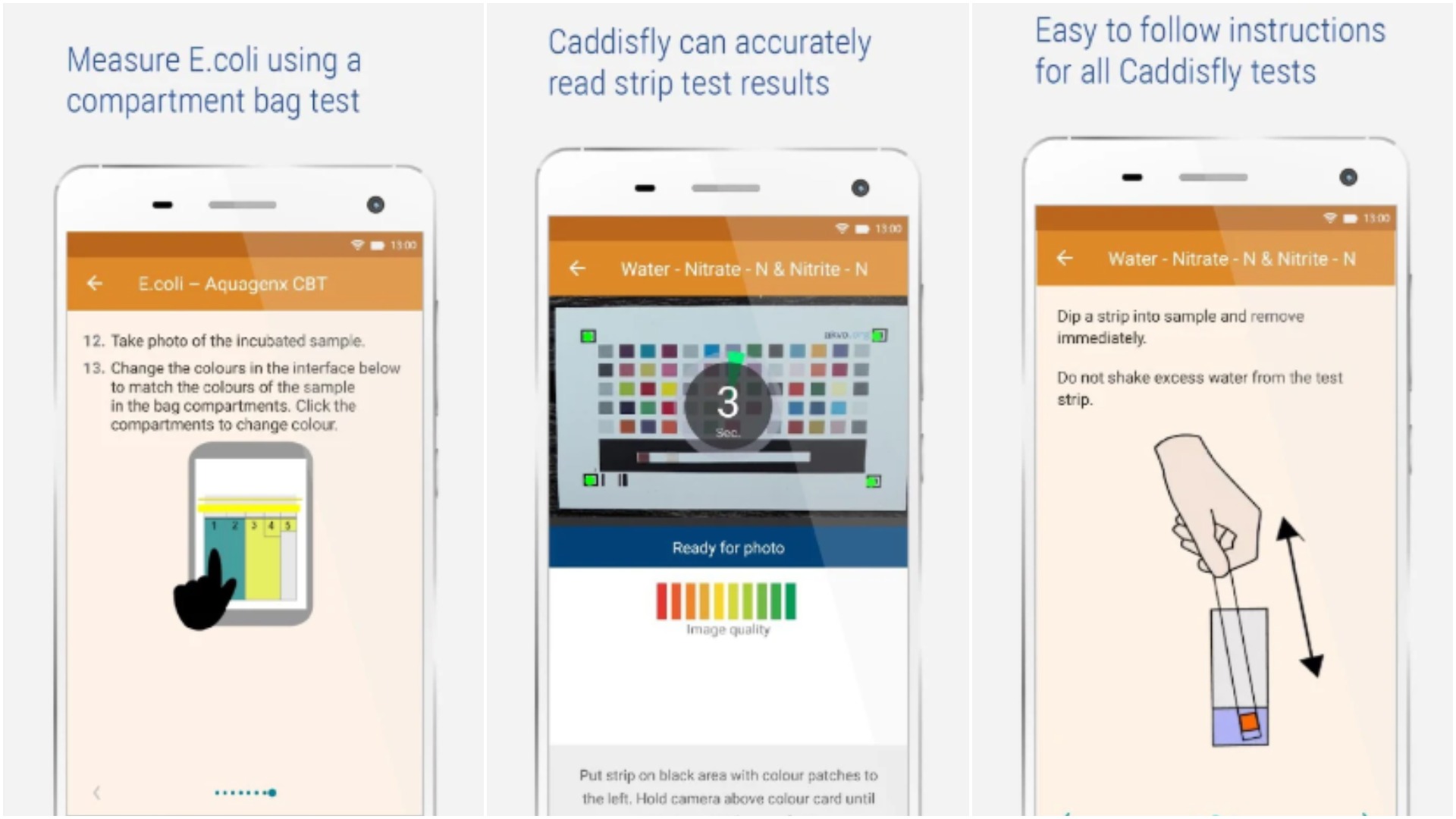
The Caddisfly app is integrated with Akvo Flow, Akvo’s online platform that collects timely, geo-tagged information, images, and data. All surveys with quantitative and qualitative information are sent to an online dashboard for rapid data analysis and decision-making.
(Disclaimer: The opinions expressed are the personal views of the author. The facts and opinions appearing in the article do not reflect the views of Devdiscourse and Devdiscourse does not claim any responsibility for the same.)
- READ MORE ON:
- Water
- Sanitation
- SDGs
- Pit Vidura
- MajiData
- PiQuant
- Fresh Life Initiative
- Akvo Caddisfly
- Hygiene
- FIRST PUBLISHED IN:
- Devdiscourse










