How Chinese brands are tightening grip on Indian smartphone market?

- Country:
- India
Being the world's second-largest smartphone market after China and one of the world's fastest-growing economies, India is a favorable and valuable market for global smartphone manufacturers. The enormous market potential India offers is propelling global players to capitalize on the opportunities. Major tech companies like Google, Samsung, Apple, Xiaomi, Lenovo, Oppo etc are ramping up their businesses and bringing in a portfolio of hardware products to leverage the huge potential that Indian market offers.
Five years ago, when the Chinese smartphone brand Xiaomi with its counterpart Vivo, Oppo forayed into India, the market was dominated by South Korean tech giant Samsung and local companies including Micromax. Within two years of their entry into the market, Xiaomi and Oppo achieved an unseen feat of market dominance and made it among the top five with market shares of 10.7 percent and 8.6 percent respectively, outsmarting home vendors and global players. The other successful Chinese brands including Vivo, Realme also share the same glorious story of success in India.
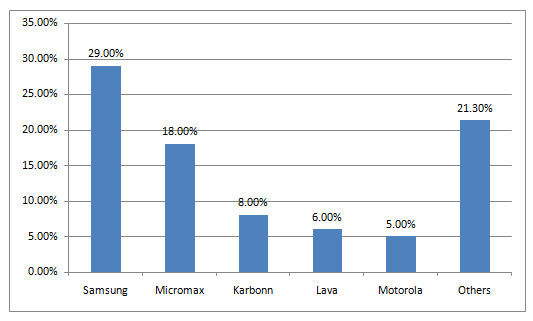
Fig: Market share of the top five smartphone brands in Q2 2014 (Source: IDC)
And now after five years, the smartphone market landscape is completely changed. As of August 2019, Xiaomi is India’s top smartphone brand with 28.3 percent market share, followed by Samsung with 25.3 percent, Vivo 15.1 percent, Oppo 9.7 percent, and Realme 7.7 percent. Chinese brands are dominant in both the online and offline channels and collectively enjoy the lion's share in the Indian smartphone market. At present, four of the five top-selling smartphone brands in India are from China. Samsung is the only non-Chinese brand amongst the top five brands that has managed to consolidate its position in the Indian market, though, Xiaomi dragged it to the second spot.
On the other hand, the US tech giant Apple that is immensely popular in the Westerns markets has failed to establish a stronghold over the Indian smartphone market because of high import duties and high prices as compared to most other smartphones sold in India. At present, iPhone's share of the Indian smartphone market is meager 1.2 percent.
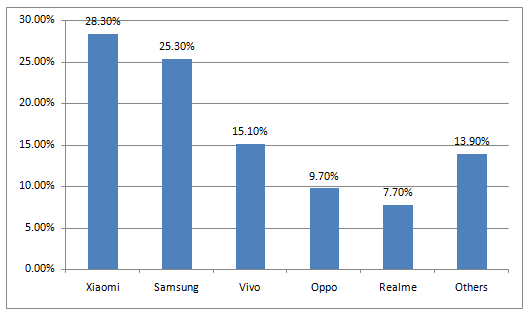
Fig: Market share of the top five smartphone brands in Q2 2019 (Source: IDC)
How Chinese brands are tightening grip on the Indian smartphone market?
Over the years, the Indian smartphone market has undergone a major transformation. From basic smartphones to foldable ones, multiple cameras, "waterfall" displays, fingerprint sensors, high-capacity batteries, super-fast processors, 4G, 5G smartphones, the evolution has been a rapid one. The way Chinese brands built their dominance is the result of innovation and planning. Of course, every brand or every business has a strategy to survive and thrive in a competitive market, but what are the top strategies that make Chinese players different from other market players? Here's a look:
Honest pricing and frontier technologies
Pricing plays a vital role in effectively targeting consumers, especially in lower-middle-income countries like India where consumers expect best-in-class mobile phones with affordable pricing. Since the advent of Chinese brands, affordability is no longer a barrier for Indian smartphone consumers as these companies continue to provide the latest technologies at reasonable prices.
"We believe that high-quality products built with cutting-edge technology should be made accessible to everyone," that's the vision and success mantra of India's number one smartphone brand Xiaomi. Since their inception, they have been continuously focusing on the budget (under 10,000) and mid-price segment Rs 15,000-Rs 20,000 which is the fastest-growing segment in India. In Q2 2019, this segment witnessed a 105.2 percent Y-o-Y growth that was largely fuelled by Chinese vendors. The Redmi Note 7 Pro which was launched earlier this year emerged as the number one selling smartphone of 2019 in the 10,000+ segment in India.
Talking about recent launches in the mid-price segment like the Xiaomi Mi A3, Realme 5 Pro, Vivo Z1 Pro, Realme 5, all these smartphones offer exceptional features like 5000mAh battery, 48-megapixel Quad Camera setup and best-in-class performance. Let’s take the more recent example, the Redmi Note 8 Pro, which is yet to make its way to India after its launch in China, is the world's first-ever smartphone commercially launched with a 64-megapixel camera and MediaTek Helio G90T chipset.
Not only in the mid-price bracket, but the Chinese vendors have a stronghold in the premium segment (USD 400-USD 600) too, which is currently the second-fastest-growing segment in India. In Q2 2019, OnePlus toppled Samsung to dominate the premium smartphone segment, owing to the high demand of OnePlus 7 series. Hence it's easy to conclude that Chinese brands are playing it right for the consumers and bringing innovative and flagship features at the minimum possible price tag. Also, Chinese players have a big hand in making India the world's second-largest smartphone market.
Make in India
Aligning with the Indian government's Make In India initiative, the Chinese players have established themselves successfully in the country. Almost all major smartphone players have their manufacturing plants in India. Xiaomi produces 95 percent of its smartphones sold in India at local manufacturing facilities and plans to take the figure to 99 percent, in the coming years.
Likewise, Oppo India produces 50 million smartphones annually at its Greater Noida manufacturing facility and seeks to double its production to 100 million smartphones by 2020. To expand its manufacturing capabilities and growth in India, Vivo has also announced plans to set up a new manufacturing facility in Uttar Pradesh with an investment of INR 4000 crore over a period of 4 years. Currently, Vivo smartphones sold in the country are manufactured at its Greater Noida facility which is one of its four manufacturing facilities globally.
Multi-brand strategy
To penetrate markets faster and accelerate expansion, not only in India but globally, Chinese smartphone vendors are following multi-brand strategy. Chinese tech giants have already tasted success with the sub-brand strategy in India. Xiaomi Group launches its smartphones under 3 brands Mi, Redmi and newly-formed Poco. While Mi is focused on mid- to high-end smartphone markets and new retail channels, Redmi is committed to developing cost-effective smartphones with the latest technology. POCO also made its debut last year with the launch of POCO F1 smartphone.
Realme, one of the top five smartphone brands in India was launched as a sub-brand of Oppo until its separation in 2018. Though, Realme now operates as an independent company. Other Chinese brands like Vivo, Huawei have also introduced their sub-brands to increase their market share.
Online-to-Offline Commerce
Striking the right balance between online and offline marketing channels is the key driver for continued growth and this is what Chinese vendors have been doing in India. For example, Xiaomi has been effectively executing its online-only sales strategy, since its inception in India. The company has always prioritized word-of-mouth marketing rather than spending heaps of money on traditional marketing methods. Xiaomi effectively uses social networking platforms to promote its products, interact with fans or the Mi Community, seek feedback to improve its products. However, it's equally important to target the offline channel and realizing this Xiaomi began its offline journey in 2017 and plans to open 10,000 physical stores by the end of this year. In the second quarter of 2019, the company led the online channel with a market share of 46.5 percent, while the offline channel accounted for 39.5 percent of Xiaomi's total shipment.
Similarly, with a strong offline presence in over 70,000 retail outlets, Vivo, last month, forayed into the online smartphone market. "We recognize the importance of both the mediums and believe no brand can be successful in the highly competitive Indian market without reaching out to its consumers – whether they are present online or offline," Vivo India Director (Brand Strategy) Nipun Marya says.
India-first launch strategy
To capture consumer space and stand out in a highly competitive market, Chinese phone makers are also using the India-first strategy for rolling out their products. Recently, Oppo Reno 2 series made its global debut in India. Likewise, the highly popular Redmi Note 7 Pro was first rolled out in India and later in China.
FDI norms relaxed: What's next?
Now that the Indian government has eased foreign direct investment (FDI) norms for several industries, the smartphone business is also set to witness a boom with the global value chains seeking to set up a manufacturing base in India. Under the relaxed norms, single-brand retailers can now do online trading prior to the opening of physical stores. US tech giant Apple that has been facing stiff competition from Chinese vendors now has a golden opportunity to expand its footprint and drive up market share. As of now, Apple sells its products through e-commerce platforms like Flipkart, Amazon and authorized retailers across the country. But now, the iPhone maker can sell products via its own online stores prior to opening offline retail stores. In the coming few years, the Indian smartphone market is set to witness much more competition and it will be interesting to watch who wins the fierce smartphone race in India.
(Disclaimer: The opinions expressed are the personal views of the author. The facts and opinions appearing in the article do not reflect the views of Devdiscourse and Devdiscourse does not claim any responsibility for the same.)
- FIRST PUBLISHED IN:
- Devdiscourse
ALSO READ
Khalid created social media narratives to influence bail hearings: Delhi Police to court
Amazon owes $525 mln in cloud-storage patent fight, US jury says
Five in Nanded booked for hurting religious sentiments on social media: Police
Amazon owes $525 mln in cloud-storage patent fight, US jury says
Exploring the Connection Between Social Media and Youth Mental Health










